Building a high-quality prospect list on LinkedIn is often the first step in any successful B2B sales or recruiting campaign. But for many professionals, this "first step" turns into a stumbling block that lasts for days.
If you have ever spent an afternoon manually copying names, job titles, and company URLs from LinkedIn search results into a spreadsheet, you know the pain. It is tedious, mind-numbing work. You open a profile, copy the name, switch tabs, paste it. Switch back, copy the URL, switch tabs, paste it. Repeat this 50, 100, or 500 times, and your brain starts to melt.
The worst part? It is not just boring—it is inefficient and prone to error.
In this guide, we will show you how to automate this entire process using Lection, an AI-native web scraping tool that lives in your browser. By the end of this article, you will know how to turn any LinkedIn search result page into a structured Google Sheet in minutes, without writing a single line of code.
The Problem with Manual Prospecting
Before we dive into the solution, let's look at why the manual approach—or "copy-paste prospecting"—is fundamentally broken for modern teams.
1. The Time Cost
Let's do the math. Even if you are fast, copying all the relevant details for a single lead (Name, Title, Company, URL, Location) takes about 60–90 seconds. To build a modest list of 100 prospects, you are looking at 2.5 hours of uninterrupted, focused work. That is nearly half a workday spent on data entry, not selling or recruiting.
2. The Accuracy Gap
When you are on your 75th copy-paste action, attention slips. You might paste a LinkedIn URL into the "Job Title" column or mistype a company name. These small errors corrupt your CRM data and can lead to embarrassing mistakes later, like addressing a CEO by the wrong title in an outreach email.
3. Burnout and Morale
High-performing sales reps and recruiters want to close deals and find talent, not act as human data pipelines. Forcing them to spend hours on manual entry leads to "low-level anxiety" and burnout. It drains the creative energy needed for crafting personalized outreach messages.

The Solution: AI-Native Web Scraping
For a long time, the only alternative to manual work was complex programming. You had to know Python, understand HTML structures, and build fragile scripts using libraries like Selenium or Puppeteer. If LinkedIn changed a class name in their code (which they do often), your script would break.
Lection change the game.
Lection is different because it uses AI to "see" the webpage just like you do. It identifies lists, recognizes patterns, and understands what data matters—whether it's on LinkedIn, Amazon, or a niche industry directory.
-
No Code Required: You don't need to be a developer.
-
Visual Selection: Just point and click.
-
Resilient: It adapts to minor layout changes automatically.
-
Resilient: It adapts to minor layout changes automatically.

Step-by-Step: Scraping LinkedIn Search Results
Let's walk through a real-world scenario. Imagine you are a sales development representative (SDR) looking for "VP of Marketing" profiles in the software industry.
Step 1: Install Lection
First, you need the tool. Head over to the Chrome Web Store and install the Lection extension. It takes seconds and pin to your browser toolbar for easy access.
Step 2: Run Your Search on LinkedIn
Navigate to LinkedIn and perform your search. You can use the free search or Sales Navigator; Lection works on both.
For this example, type "VP Marketing" in the main search bar, filter by "People," and maybe add a location filter like "San Francisco Bay Area." You should now see a list of profiles.
Step 3: Activate Lection
Click the Lection icon in your browser toolbar to open the sidebar. Lection's AI will immediately start analyzing the page.
Because you are on a search results page, Lection will likely detect a "List" automatically. It will highlight the repeating elements (the user profiles) and suggest them for extraction.
Step 4: content Selection and Refinement
Lection allows you to visually confirm what you want to extract. You can verify that it is capturing:
- Name
- Headline / Job Title
- Location
- Profile URL
If you want to capture specific text that wasn't automatically selected, simply click on it. Lection learns from your interactions.
Step 5: Handle Pagination
This is where Lection truly shines. A LinkedIn search might have 100 pages of results. You don't want to scrape just the first page; you want all of them.
Lection has built-in pagination handling. You can set it to identifying the "Next" button and automatically click through to the next pages, extracting data as it goes. You can set a limit (e.g., "Scrape 10 pages") or let it run until the end.
[!NOTE] Safety First: When scraping sites like LinkedIn, it is crucial not to act like a bot that clicks 100 times a second. Lection includes smart delays to mimic human reading speed, keeping your account safer.
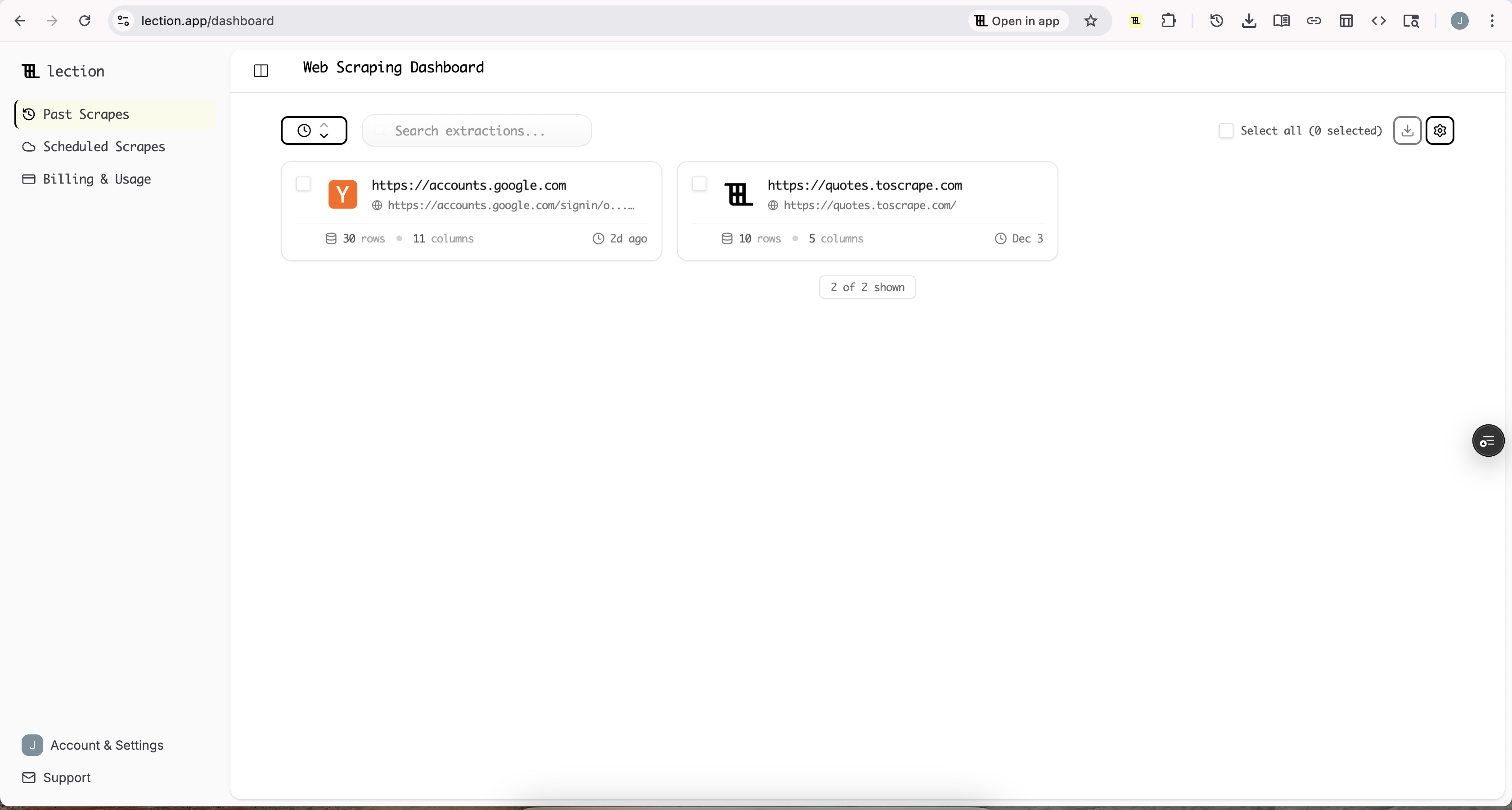
Step 6: Export Your Data
Once the scrape is complete, you will have a clean, structured table of data right in the Lection sidebar.
From here, you can:
- Download as CSV/Excel: Perfect for manual upload to a CRM.
- Sync to Google Sheets: Send the data directly to a collaborative sheet.
- Send to Webhook: Integrate with Zapier or Make.com to trigger automated workflows.
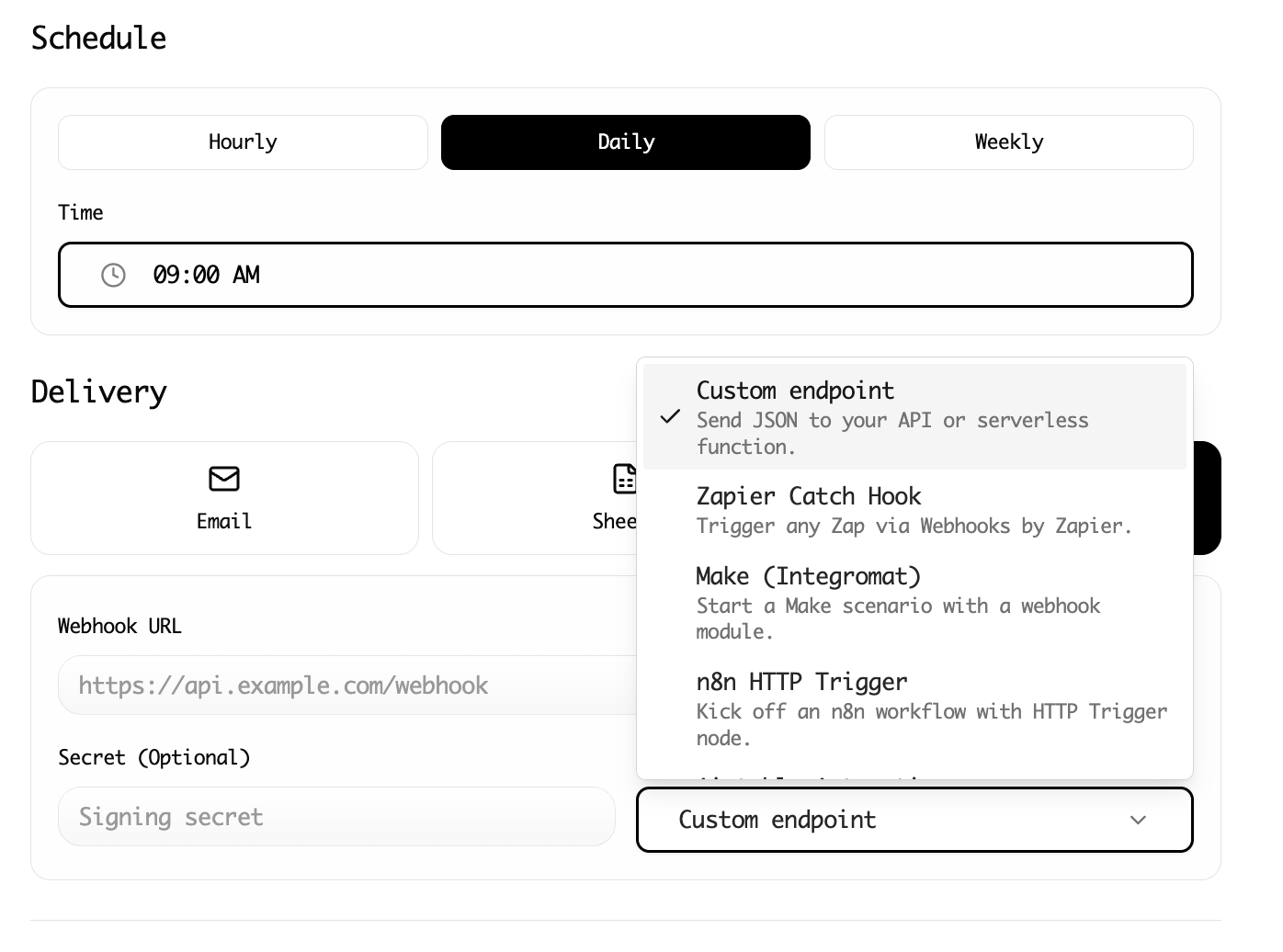
Advanced Workflow: Cloud Scraping
Running a scraper on your local machine is great for ad-hoc tasks, but what if you need to monitor new job postings or fresh profiles every week?
Lection offers Cloud Scraping. This allows you to offload the task to Lection's cloud servers. You can schedule the scrape to run every Monday morning at 8:00 AM, so a fresh list of leads is waiting for you when you start work—without you needing to open your browser.
Troubleshooting Common Questions
"Will I get banned from LinkedIn?" LinkedIn is strict about automation. While no tool can guarantee 100% immunity, Lection is designed to be safer than raw scripts. By running in your browser with human-like delays, it mimics natural behavior. However, always be conservative—don't try to scrape 10,000 profiles in an hour. Start small and build up.
"Can I scrape emails?" LinkedIn typically does not display email addresses on the public search result page. Lection scrapes what is visible. To get emails, you typically need to visit the individual profile (which Lection can automate via "Deep Scraping" or crawling) or use a data enrichment tool after you have the names and companies.
"Does this work on Sales Navigator?" Yes! Sales Navigator often has cleaner, more structured data, and Lection works excellently with it.
Why Lection is the Best Choice for 2025
There are other tools out there, but many are stuck in the past.
- Vs. Traditional Scrapers: Tools like Octoparse force you to learn a complex interface. Lection is intuitive.
- Vs. Python Scripts: Python requires maintenance. If LinkedIn updates a class name, your script breaks. Lection's AI adapts to visual changes, making it far more robust.
- Vs. Manual Work: There is no comparison. Lection is 100x faster and infinitely more accurate.
Conclusion
The days of manual data entry are over. In 2025, your value lies in connecting with people, not copying their names.
By using Lection, you reclaim hours of your week. You ensure your data is accurate, your CRM is clean, and your sanity is preserved.
Ready to automate your prospecting? Install Lection for free and start building your first dataset in minutes.