You have a Google Sheet that tracks competitor prices, job postings, real estate listings, or product inventory. Every morning, you manually browse websites, copy data, paste it into cells, and hope you did not miss anything. By Thursday, the task feels like drudgery. By month-end, the spreadsheet is half-updated and unreliable.
Before building automated data pipelines, you need to understand why the obvious solutions do not work. Otherwise, you will waste hours troubleshooting problems that cannot be fixed.
The IMPORTXML and IMPORTHTML Problem
Google Sheets includes built-in functions for pulling web data:
IMPORTXMLextracts data using XPath queriesIMPORTHTMLpulls tables or lists from web pages
In theory, perfect. In practice, deeply frustrating.
These functions fail on JavaScript-rendered websites. When a website loads content dynamically (which most modern sites do), IMPORTXML sees only the initial HTML skeleton, not the data you actually want. You get the dreaded "Imported content is empty" error.
A marketing analyst at a mid-sized agency recently described their experience: "I spent two hours crafting the perfect XPath query for a competitor's pricing page. It worked once. The next morning, the formula returned nothing. The site had not even changed; it just loaded their prices with JavaScript."
Additional limitations compound the problem:
- 50,000 URL limit across all import functions per document
- Hourly refresh intervals that cannot be controlled or scheduled
- No authentication support for pages requiring login
- Caching issues that display stale data
- "Result too large" errors when extracting larger datasets
For a deeper dive into these failures, see our guide on when IMPORTXML breaks and what to do instead.
Google Apps Script: Powerful but Complex
Google Apps Script offers more flexibility. You can write JavaScript that fetches pages, parses content, and writes to your sheet. You can even schedule scripts to run automatically using time-driven triggers.
The problem is that Apps Script requires actual programming knowledge. You need to understand HTTP requests, DOM parsing, regular expressions, and the Apps Script API. For non-developers, this is not a realistic solution.
Even for developers, maintaining Apps Script scrapers becomes tedious. Website structure changes break parsers. Rate limiting requires careful handling. Error recovery needs custom logic. What started as "just a quick script" becomes an ongoing maintenance headache.
Third-Party Add-ons: Hit or Miss
The Google Workspace Marketplace offers scraping add-ons with names like "SheetMagic," "ImportFromWeb," and similar tools. Some work reasonably well for simple cases. But they share common limitations:
- Most cannot handle JavaScript-rendered content
- Scheduling often requires premium subscriptions
- Customer support ranges from slow to nonexistent
- Privacy concerns arise when add-ons access your spreadsheet data
The market for Google Sheets scraping add-ons is filled with abandoned projects and mediocre tools. Finding one that actually works reliably takes trial and error.
The Modern Approach: Browser-Based Scraping with Cloud Scheduling
The solution is to use a tool that works within a real browser environment (handling JavaScript naturally), operates visually without coding, and offers true cloud scheduling with direct Google Sheets delivery.
Lection is designed precisely for this workflow. It runs as a Chrome extension, extracting data from any website you can view in your browser. When you set up cloud scraping, Lection runs your extractions on a schedule and sends results directly to your Google Sheet, no manual intervention required.
Here is how to set it up.
Step-by-Step: Automating Google Sheets with Lection
This walkthrough creates an automated data pipeline that extracts web data and updates your spreadsheet on a recurring schedule.
Step 1: Install the Lection Chrome Extension
Visit the Chrome Web Store and add Lection to your browser. The extension activates automatically on any webpage.
Step 2: Navigate to Your Target Website
Open the website containing the data you want to track. This could be:
- A competitor's product listings
- A job board with relevant openings
- Real estate listings in your market
- E-commerce prices you need to monitor
- Any data source that updates regularly
For this example, imagine you are tracking product prices from an e-commerce site.
Step 3: Select Data with Point-and-Click
Click the Lection extension icon. The interface opens, and you can click on data elements you want to extract. Lection uses AI to understand the page structure. When you select one product price, it recognizes the pattern and offers to extract all similar prices on the page.
No XPath queries. No CSS selectors. Just click on what you want.
Step 4: Configure Data Fields
Name your data columns meaningfully. Instead of "Field 1," use "Product Name," "Price," "Availability," etc. Clear naming makes your spreadsheet immediately usable when data arrives.
Step 5: Test the Extraction
Run a test extraction to verify the data looks correct. Check that all rows are captured and fields are properly aligned. Make adjustments if needed.
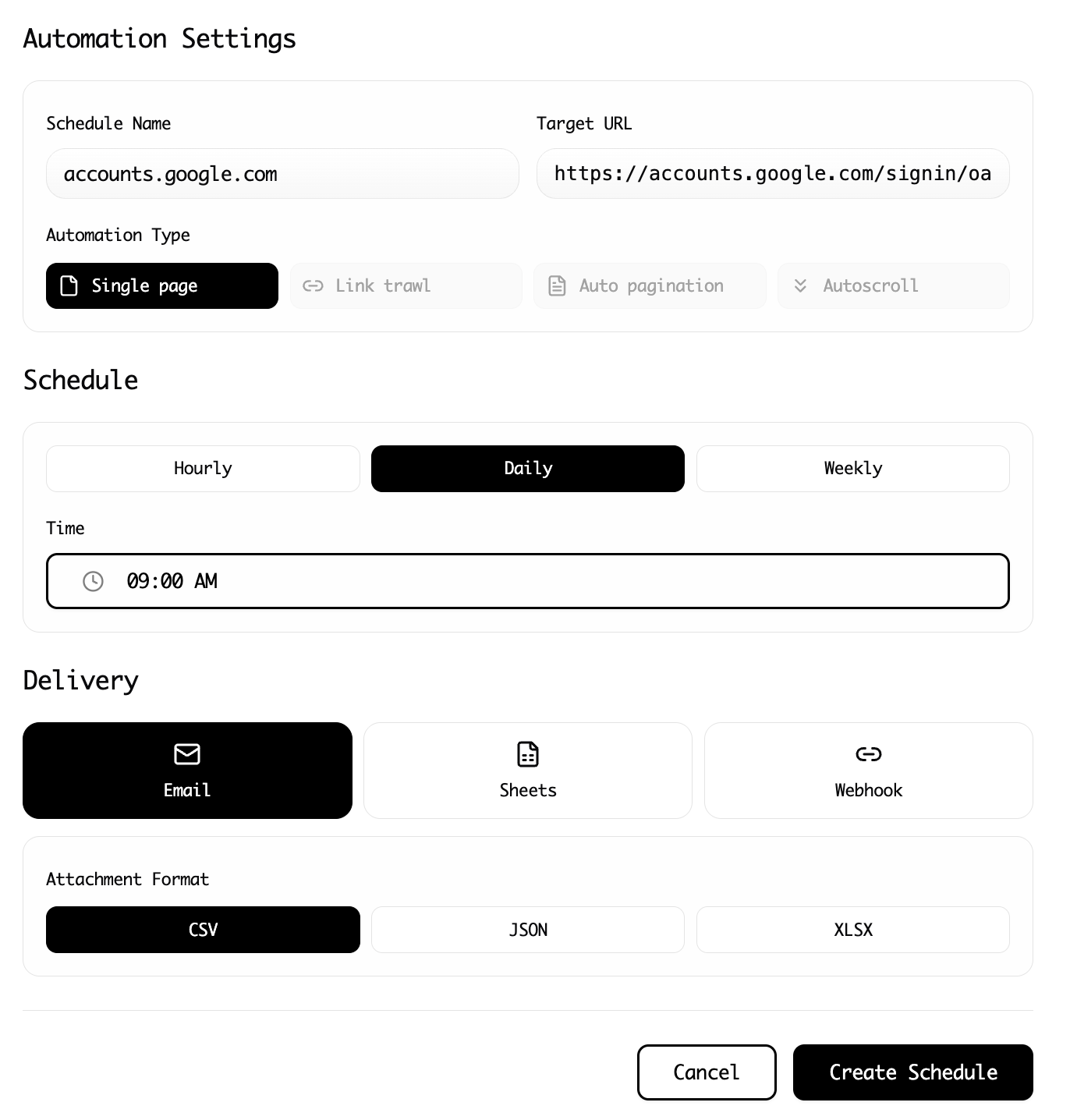
Step 6: Enable Cloud Scraping
With your extraction configured, enable cloud scraping. This moves the extraction from your local browser to Lection's cloud infrastructure. Your computer does not need to be on for the scrape to run.
Step 7: Set Your Schedule
Choose how often the extraction should run:
- Every hour for rapidly changing data like stock prices or inventory levels
- Daily for price monitoring, job postings, or news tracking
- Weekly for slower-moving datasets
The schedule runs automatically. You set it once and forget it.
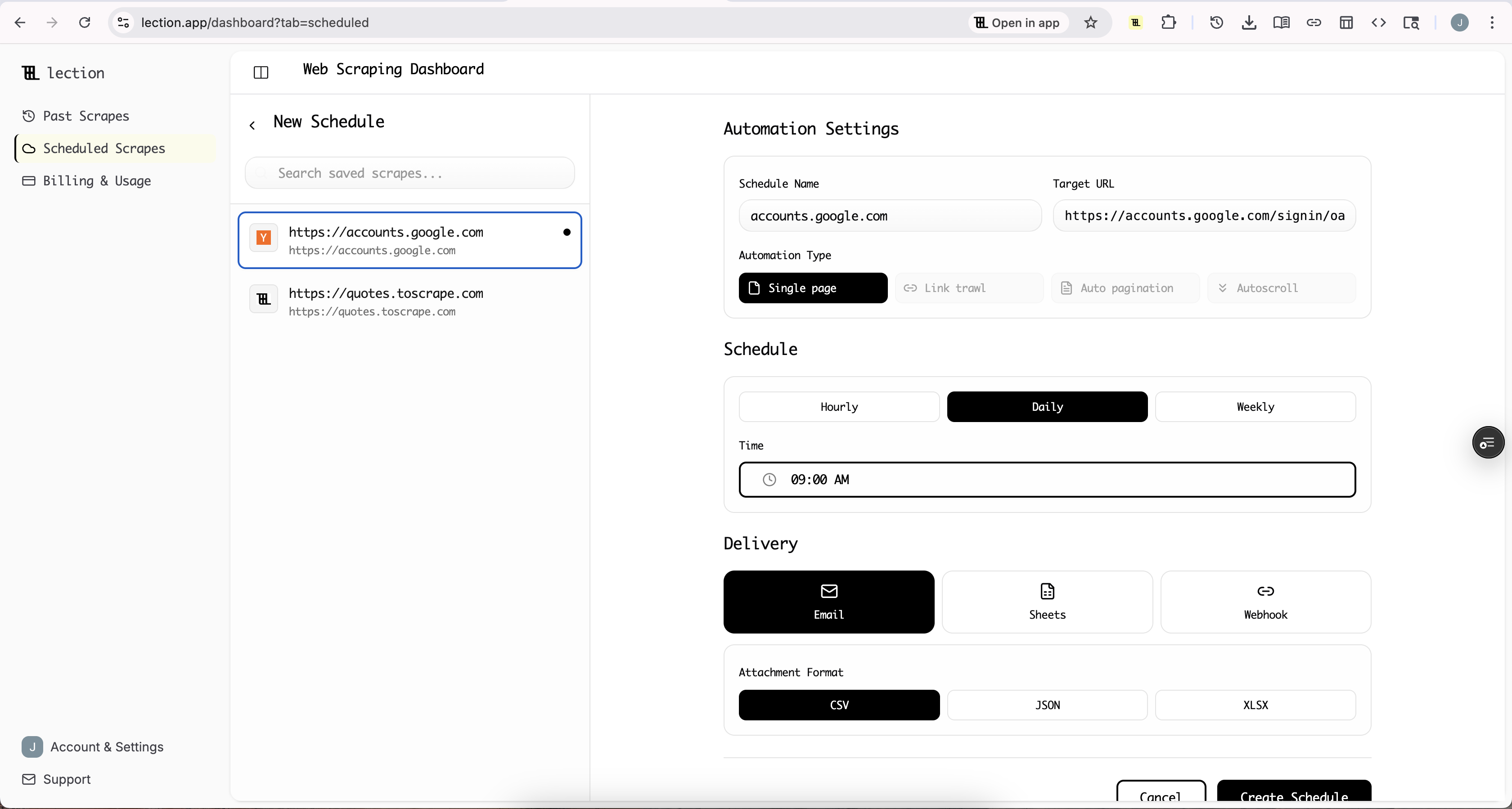
Step 8: Connect Google Sheets
Select Google Sheets as your delivery destination. Lection prompts you to authorize access to your Google account. Once connected, choose an existing spreadsheet or create a new one.
You can configure whether new data should:
- Append to existing rows (builds a historical dataset)
- Replace existing data (always shows current state)
For price tracking, appending creates a historical record. For inventory monitoring, replacing keeps the sheet current.
Step 9: Verify the First Run
After your first scheduled run completes, open your Google Sheet. The data should appear in the columns you defined. Each subsequent run adds or updates data according to your configuration.
If something looks off, adjust your extraction and re-test. The visual interface makes iteration fast.
Advanced Configuration Options
Once basic automation is working, consider these enhancements.
Pagination and Multi-Page Scraping
Many datasets span multiple pages. Lection handles pagination automatically. Configure how many pages to traverse, and each scheduled run extracts from all of them. A job board with 20 pages of listings becomes a single automated extraction.
Deep Link Trawling
Sometimes you need data from individual detail pages, not just listing pages. Deep link trawling follows links from a listing page to each detail page, extracting additional fields. For example, scrape a list of product categories, then automatically visit each product page to extract descriptions, specifications, and reviews.
Multiple Delivery Destinations
Beyond Google Sheets, Lection can send data to:
- Webhooks for custom integrations
- Zapier for thousands of app connections (see our Zapier web scraping guide)
- Make for visual automation workflows (see our Make integration tutorial)
- Notion for knowledge management (see sending scraped data to Notion)
Data Validation and Transformation
Clean data is critical for downstream analysis. Lection includes validation options to ensure extracted data meets formatting requirements before it reaches your spreadsheet.
Real-World Use Cases
Abstract automation is hard to visualize. Here are concrete examples of automated Google Sheets pipelines.
Price Monitoring Dashboard
A small e-commerce business tracks competitor prices across five competing websites. Previously, an intern spent three hours every Monday morning manually checking prices and updating a spreadsheet. Now, a scheduled Lection extraction runs daily at 6 AM, populating a Google Sheet with current competitor prices. When the team arrives, the data is ready.
The same data feeds into simple Google Sheets conditional formatting that highlights when competitors drop prices, enabling fast response to market changes.
Real Estate Market Tracker
A real estate investor monitors listings in three target neighborhoods. Every afternoon, new listings from Zillow, Redfin, and local MLS feeds appear in a master spreadsheet. The investor receives a daily summary via a connected email notification (set up via Zapier). Promising properties are flagged for investigation before the competition even sees them.
For details on this workflow, see our Amazon product data to Google Sheets guide, which applies similar principles.
Job Posting Aggregator
A recruiting firm tracks job postings across LinkedIn, Indeed, and niche industry job boards. Automated extractions run every four hours, catching new postings within half a day of publication. Recruiters spend their time reaching out to candidates rather than manually browsing job sites.
Related: How to scrape LinkedIn without code
Content Research Feed
A content marketing team monitors competitor blogs, industry news sites, and social media for content inspiration. Daily extractions capture headlines, publication dates, and URLs. The team reviews a curated feed in Google Sheets each morning, spotting trends before they peak.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even well-configured automation occasionally needs attention.
Data Stopped Appearing
If scheduled runs stop producing data:
-
Check if the website changed. Sites redesign pages, restructuring the HTML that Lection relies on. Re-run the extraction manually. If it fails, reconfigure the selectors.
-
Verify your cloud scraping subscription is active. Cloud features require a paid plan.
-
Check Google Sheets permissions. If you revoked Lection's access, reconnect the integration.
Duplicate or Missing Rows
If data appears duplicated or incomplete:
-
Review your append/replace settings. Appending on every run creates duplicates if you want current-state-only data.
-
Check pagination settings. Missing rows might mean pagination is not traversing all pages.
-
Verify rate limiting. Some aggressive targets block requests. Lection handles this gracefully, but verify the site is not blocking access.
Data Format Issues
If extracted data appears malformed:
-
Check the source website. Sometimes the website itself has formatting issues.
-
Use Lection's data transformation options to clean values before they reach your sheet.
-
Consider a Google Sheets formula to post-process data after import.
Comparison: Lection vs. Alternatives
How does this approach compare to other Google Sheets automation methods?
| Method | Handles JavaScript | True Scheduling | No Code Required | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMPORTXML/IMPORTHTML | No | No (hourly auto-refresh only) | Yes | Low |
| Google Apps Script | With complexity | Yes | No | Medium |
| Third-party add-ons | Varies | Varies | Usually | Medium |
| Lection | Yes | Yes | Yes | High |
The key differentiator is that Lection operates in a real browser environment, naturally handling JavaScript-rendered content that causes other tools to fail. Combined with visual configuration and true cloud scheduling, it eliminates the technical barriers that make other approaches frustrating.
The ROI of Automation
Quantifying time savings clarifies the value of automated data pipelines.
Consider a marketing analyst who spends 45 minutes daily updating a competitive tracking spreadsheet. That is 3.75 hours per week, or roughly 195 hours per year. At a loaded labor cost of $50/hour, that is $9,750 annually for one manual data collection task.
Automated extraction takes 30 minutes to configure once, plus occasional 5-minute checkups. The yearly time investment drops to perhaps 10 hours. That is a 95% reduction in time spent on data collection.
Beyond time savings, automation improves data quality. Manual data entry introduces errors. A tired analyst misses a row or transposes digits. Automated extraction is consistent. The 347th run is as accurate as the first.
Getting Started Today
Automating Google Sheets with scraped data requires three things:
- A data source that updates regularly and contains information you need
- A scraping tool that handles modern websites reliably
- A scheduling mechanism that runs without manual intervention
Lection provides the second and third components in a unified package. The AI-powered extraction handles any website you can view in your browser. Cloud scraping runs extractions on your schedule. Direct Google Sheets integration delivers data where you need it.
Ready to stop manually updating spreadsheets? Install Lection and set up your first automated data pipeline in minutes.